What Are Molecular Compounds Formed From
Some elements in Group 15 of the periodic table form compounds of the type AX 5. However many halogenated organic compounds of high molecular weight in particular those containing several halogen atoms per molecule are nonflammable.

Science Infographic Ionic And Molecular Compounds Infographicnow Com Your Number One Source For Daily Infographics Visual Creativity Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.

What are molecular compounds formed from. A chemical formula plural. A trigonal bipyramidal shape forms when a central atom is surrounded by five atoms in a molecule. The other two atoms are on opposite ends of the molecule.
Examples of compounds included under the same type are listed below. The properties of compound are different from the properties of the elements from which it is formed. Ionic compounds are usually formed when a metal reacts with a nonmetal or a polyatomic ion.
Binary molecular covalent compounds are formed as the result of a reaction between two nonmetals. Differences between Ionic and Molecular Compounds An ionic compound is formed by the reaction of a metal with a non-metal whereas a molecular compound is usually formed by the reaction of two or more non-metals. Molecular compounds are electrically neutral.
In the kinetic theory of gases the term molecule is often used. Some are in fact used as fire retardants. Aluminum bromide Al 2 Br 6.
Whereas ionic compounds are usually formed when a metal and a nonmetal combine covalent compounds are usually formed by a combination of nonmetals. In quantum physics organic chemistry and biochemistry the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A compound is formed as a result of chemical reaction between the constituent elements.
A compound is a substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion by mass. In fact all types of hydrocarbons are molecular or covalent compounds as they are formed by combining carbon and hydrogen gases both nonmetals in different ratios. Although there are no ions in these compounds they are named in a similar manner to binary ionic compounds.
Usually molecular compounds are insoluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents. The low-molecular-weight materials gases and liquids are generally dangerously flammable. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols which.
In the geometry three atoms are in the same plane with bond angles of 120. Since hydrogen is a nonmetal binary compounds containing hydrogen are also usually covalent compounds. Under normal conditions molecular compounds often exist as gases low-boiling liquids and low-melting solids although many important exceptions exist.
Covalent compounds are formed when two nonmetals react with each other. The flammability of these materials is variable. Under normal conditions molecular compounds often exist as gases low-boiling liquids and low-melting solids although many important exceptions exist.
Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge. Formulae is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule using chemical element symbols numbers and sometimes also other symbols such as parentheses dashes brackets commas and plus and minus signs. Examples include PCl 5 and AsF 5.
The nomenclature of binary covalent compounds follows these. A classic example of molecular compound is hydrocarbon. Whereas ionic compounds are usually formed when a metal and a nonmetal combine covalent compounds are usually formed by a combination of nonmetals.

2 6 Molecules And Molecular Compounds Atom Diagram Chemistry Textbook Chemistry

Elements Mixtures And Compounds Vs Atoms And Molecules School Chemistry Elements Compounds And Mixtures Compounds And Mixtures Chemistry Activities

Ionic Vs Molecular Compounds Final Gcse Chemistry Chemistry Study Guide Physical Science

Polarity Of Molecular Bonds Ionic Crystalline Structure Water Soluble Conductive Covalent Soft S Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom
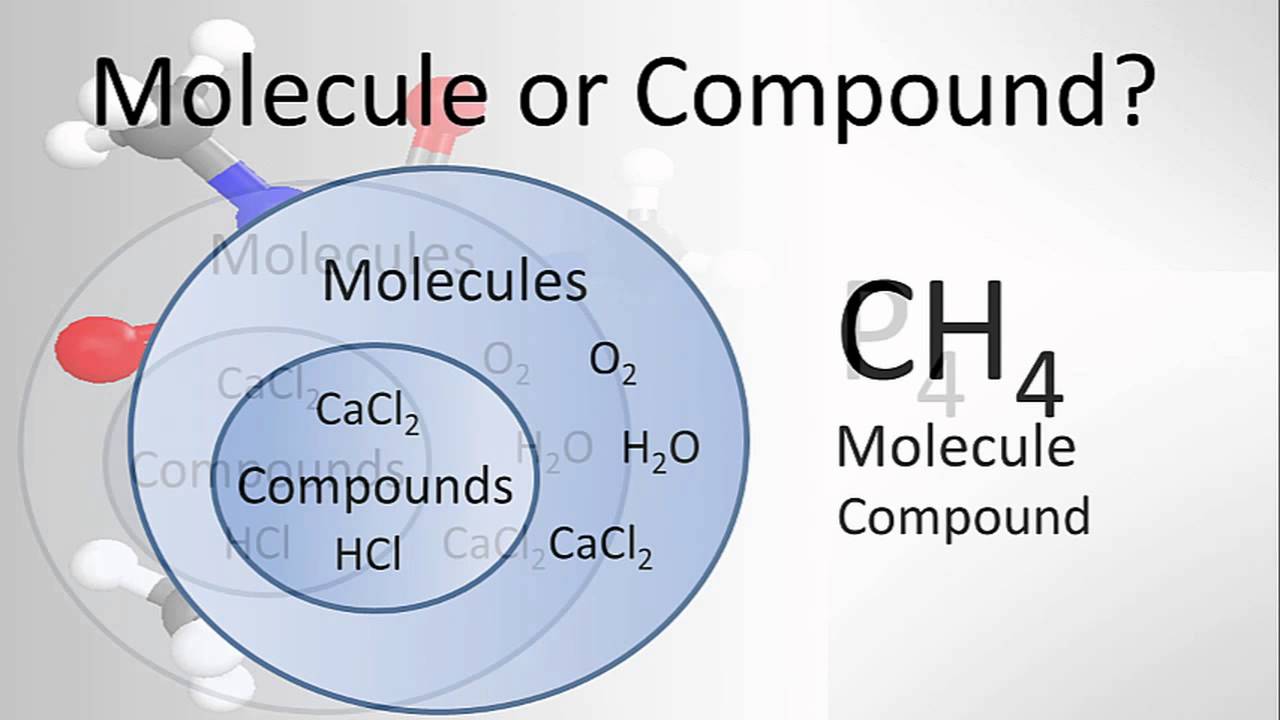
Molecule Vs Compound Examples And Practice Molecules Middle Science Homeschool Science

Molecular Compounds Clip Art Teaching Homeschool Chemistry Lessons Science Curriculum

Difference Between Ionic And Molecular Compounds Infographic Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom Study Chemistry

Elements Atoms Molecules Ions Ionic And Molecular Compounds Cations Vs Anions Chemistry Youtube Compounds Science Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons

Chemistry Lesson Identifying Ionic Vs Molecular Compounds Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Worksheets Chemistry

Chemical Bonding Science Doodle Note Activity Video Doodle Notes Science Doodle Notes Science Doodles

Molecules Spacefilledmodels Space Filled Models Are Useful Because They Show The Elements Relative Size And It Give A C Science Education Molecules Molecular

Tetryonics 56 01 Tetryonic Molecular Bonding Is Based On The Physical Charged Topologies Of Chemical Elements And They Come Together And Form Complex Molecula

Difference Between Element Molecule And Compound Definition Periodic Table Types Relationship And Diff In 2021 Chemistry Education Biology Facts Teaching Chemistry

Chemical Bonding Piktochart Visual Editor Chemistry Classroom Science Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Difference Between Empirical And Molecular Formula Infographic Chemistry Basics Chemistry Study Guide Chemistry Education

Ionic And Covalent Bonding Are Depicted In The Picture Ionic Bonds Is The Attraction Of A Cation To An An Ionic Bonding Teaching Chemistry Covalent Bonding

Matter Atoms Elements Molecules And Compounds Anchor Posters Atoms And Molecules For Kids Molecules Science Display

Section 8 1 Are Electrons Only Transferred While Studying Ionic And Metallic Bonding Electrons Have Been Mov Covalent Bonding Ionic Bonding Metallic Bonding

Compounds Molecules Compounds Form From Elements On The Periodic Table Covalent Bonding Ionic Bonding Molecules