What Are Covalent Compounds Made Of
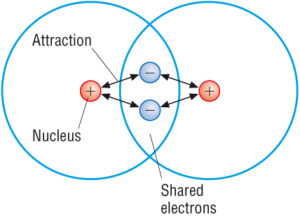
Coordinate bonds are commonly found in coordination compounds. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atomsThese electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding.

Covalent Bond An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Covalent bonding is an important and extensive concept in chemistry and it will be treated in considerable detail in a later module.
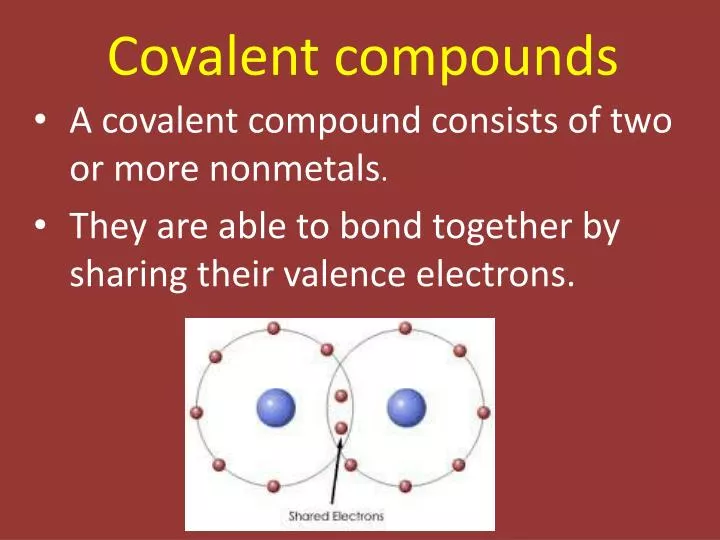
What are covalent compounds made of. Covalent compounds Ionic compounds composed of simple molecules a Have high melting and boiling points a Have low melting and boiling points b Exist as solids at room temperature. Covalent bonds only form between nonmetallic elements because these elements have the same or similar electronegativity values. Hydrocarbons are compounds that consist entirely of carbon and hydrogen linked together via covalent bonding.
It can be considered as a compound which does not contain carbon to hydrogen bond which calls C-H bond. Examples of compounds include table salt or sodium chloride NaCl an ionic compound sucrose a molecule nitrogen gas N 2 a covalent molecule a sample of copper intermetallic and water H 2 O a covalent molecule. The binding arises from the electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons.
Without stirring the food coloring will mix into the water through only the movement of the water and food coloring molecules. These compounds are composed of positive and negative ions formed by adding or subtracting electrons from neutral atoms and molecules. A bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms.
Although there are no ions in these compounds they are named in a similar manner to binary ionic compounds. Steps to Naming Covalent Compounds. A carbon atom has four electrons in its outermost valance shell that can be shared with other four atoms.
Ionic Compounds vs Covalent Compounds. These molecular compounds covalent compounds result when atoms share rather than transfer gain or lose electrons. Many covalent compounds are flexible or gaseous and are not water soluble.
This module explores two common types of chemical bonds. The nomenclature of binary covalent compounds follows these rules. Covalent bonds are highly stable bonds with low melting points.
Examples of Compounds. This is because covalent compounds do not have charged particles capable of transporting electrons. Difference Between Organic And Inorganic Compounds - Organic compound is a chemical compound of living things which contains Carbon and carbon atoms because of their relations with organisms.
If an element does not have a prefix assume that the subscript is 1 Third apply the above naming scheme. The law of constant composition can be used to distinguish between compounds and mixtures of elements. Almost all the compounds in Chemistry can be broadly categorized under ionic and molecular compounds.
Metallic compounds contain freely floating electrons which allow them to conduct electricity and heat well. Covalent compounds like sugar and food coloring can dissolve and diffuse but they do not dissociate. Walls made of paraffin wax a covalent compound help keep the temperature in a room steady as night changes into day and day into night.
If the prefix of the first element would be mono- it is not neededTIP. Inorganic compound is a chemical compound which is the opposite of an organic compound. A compound is made up of two or more elements chemically bonded together.
Here are examples of covalent compounds and a look at their common properties. What is the most important property of covalent compounds that allows paraffin wax to help keep a rooms temperature level. A coordinate covalent bond also known as a dative bond dipolar bond or coordinate bond is a kind of two-center two-electron covalent bond in which the two electrons derive from the same atomThe bonding of metal ions to ligands involves this kind of interaction.
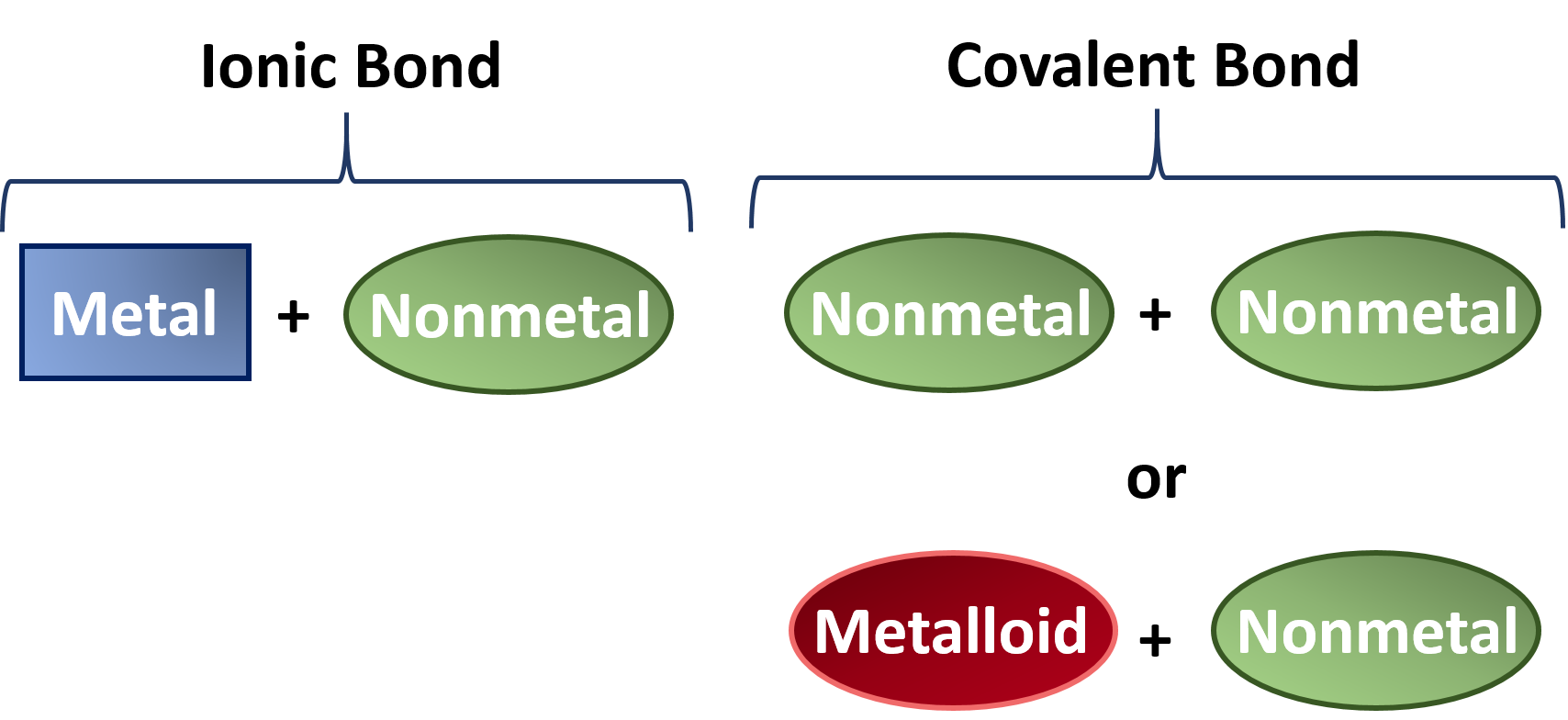
These examples show how the rules. Ionic compounds are made of ionic bonds and molecular compounds are made of covalent bonds. Binary molecular covalent compounds are formed as the result of a reaction between two nonmetals.
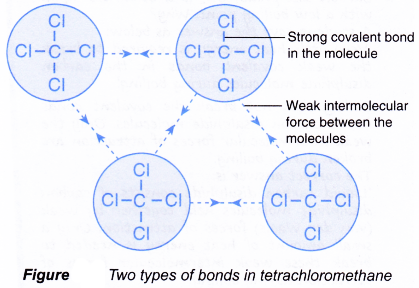
Non-volatile b Usually exist as liquids or gases at room temperature. Volatile c Conduct electricity in the molten state or in an aqueous solution but do not conduct electricity in the solid state. The atoms of covalent materials are bound tightly to each other in stable molecules but those molecules are generally not very strongly attracted to other molecules in the material.
Metals often react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. The module presents chemical bonding on a sliding scale from pure covalent to pure ionic depending on differences in the electronegativity of the bonding atoms. Ketzbook demonstrates how to draw Lewis diagrams for elements and simple molecules using an easy-to-follow step-by-step explanation with several examples.
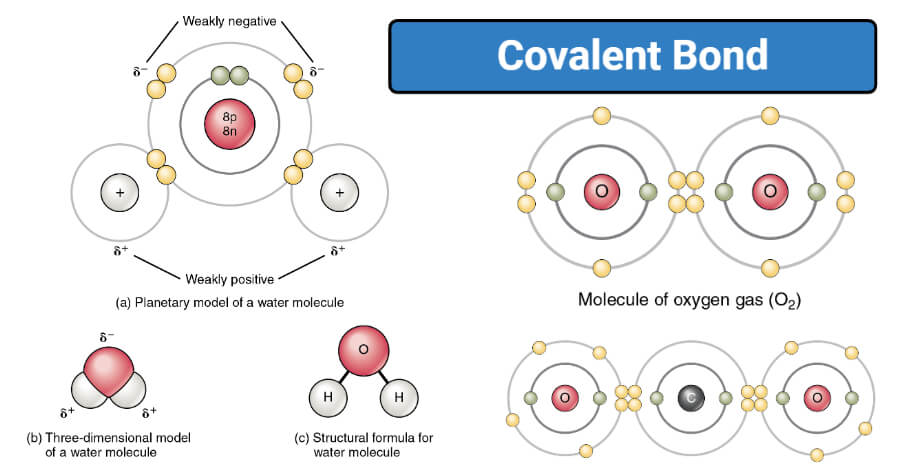
The law of constant composition states that the ratio by mass of the elements in a chemical compound is always the same regardless of the source of the compound. Double covalent bonds are usually made from nonmetals like carbon nitrogen and oxygen. Water molecules are not absolutely neutral.
This type of interaction is central to Lewis acidbase theory. Covalent compounds generally have low boiling and melting points and are found in all three physical states at room temperature. Second look at the subscript of each element to determine which prefix to use.
Mixtures do notWater is always 888 O and 112 H by. 234 is a time series of drops of food coloring diffusing in water. Depending on the energy level and closeness to the nucleus the electrons will stay within a certain shape.
Compounds have a constant composition. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity. The difference between Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compounds is their formation.
Ionic compounds tend to be crystalline structures with high melting points that are water soluble. Comparison of Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds. They differ from each other due to the bonding type between the atoms that take part in making a molecule compound.
The millions of different chemical compounds that make up everything on Earth are composed of 118 elements that bond together in different ways. Covalent bond in chemistry the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. First identify the elements present.
Covalent compounds or molecular compounds are chemical compounds made of elements connected by covalent bonds. Get used to what part of an elements. Many compounds do not contain ions but instead consist solely of discrete neutral molecules.
The Ionic Compound is formed when there is a big difference in the electronegativity of the atoms where the less electronegative atom. Because of the nature of ionic and covalent bonds the materials produced by those bonds tend to have quite different macroscopic properties. These molecules have a slight negative charge on the oxygen atom and slight positive charges on the hydrogen atoms.
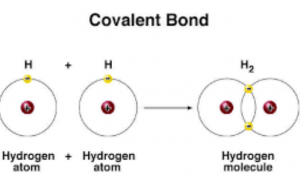
Since hydrogen is one electron short for a stable configuration it forms a covalent bond by mutually sharing one electron with. Nonmetals combine with each other to form covalent compounds which exist as neutral molecules. Electrons move freely and very fast around an atom.
Why are covalent compounds not soluble in water. Chemical compound - chemical compound - Binary molecular covalent compounds. On the other hand we know that the covalent compounds are made up of neutral molecules or molecules with slight charges.
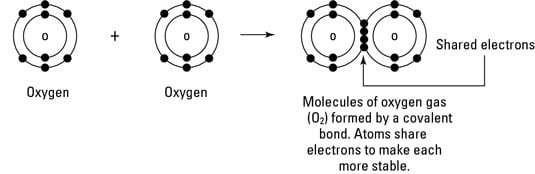
Here is a list of examples of compounds made of two elements. For many molecules the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence.

Covalent Bond Definition Types And Examples
What Does A Covalent Bond Mean Quora

Covalent Bond An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Covalent Bonding Biology Definition Role Expii

Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Covalent Bond Definition Properties Types Formation Examples
What Are The Types Of Covalent Bonds Science Online
Environmental Science What Is Covalent Bonding Dummies

Covalent Bond Examples Formation Properties What Is A Covalent Bond Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Covalent Compounds Covalent Bond Properties Examples With Videos

Covalent Bonds Biology For Majors I

Covalent Bond Definition Types And Examples

Covalent Bond Definition Properties Examples Facts Britannica
Covalent Compounds Covalent Bond Properties Examples With Videos

Covalent Bonding Gcse The Science Hive
Ppt Covalent Compounds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5168896
Properties Of Ionic And Covalent Compounds A Plus Topper

Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
